Wind Turbines Types
Wind Turbines can be classified into the Vertical Axis type (a) and the Horizontal Axis type (b). Most modern wind turbines use a horizontal axis configuration with two or three blades, operating either downwind or upwind.
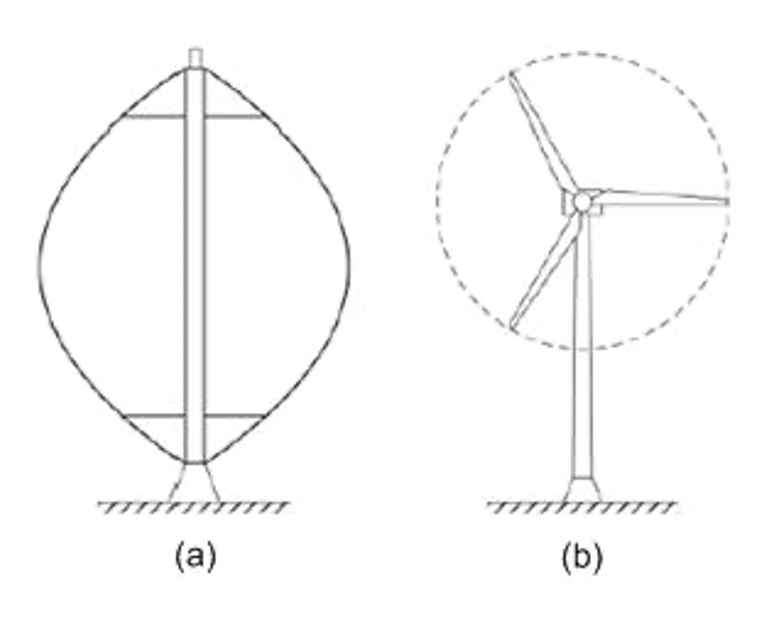
The main advantage of Vertical Axis wind turbines is that the gearbox and transmission systems are placed at ground level. Another advantage is their ability to capture the wind without considering wind direction. However, maintenance of these turbines is not straightforward as removing the rotor is often required. In addition, the captured energy is not efficient and large areas are compulsory for those turbines situated on land as guy-wire is necessary for supporting the structure.
Alternatively, the most recent wind turbines used are Horizontal Axis based with two or three blades. Having the rotor positioned on the top of the tower creates a more efficient system as more wind energy is produced. These turbines also have a nacelle, which held up by the tower and contains the gearbox and generator. A yaw system, which is turning the nacelle and rotor to face the wind, enables the turbine to capture the highest amount of energy. Additionally, some wind turbine blades have moveable blade tips, which are used as air brakes.